|
What to know before starting? What to know before starting?
 What will you learn? How much time will it take? EQF level Who created the content and will recognise your learning? Let’s start... but first a Video
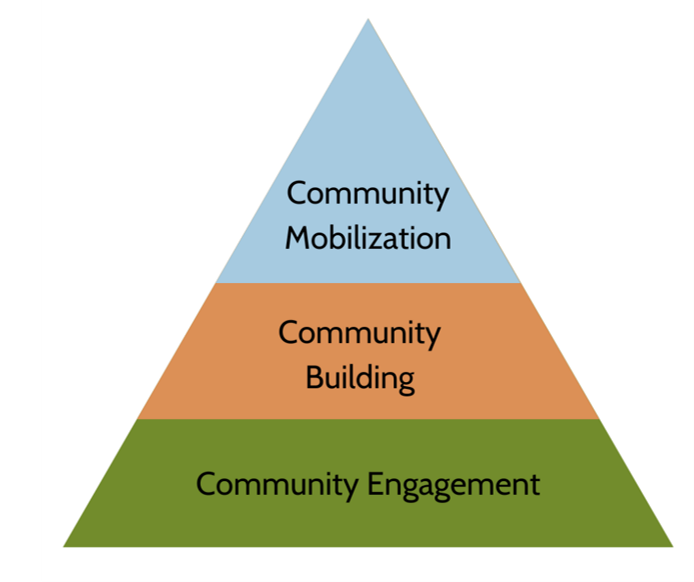
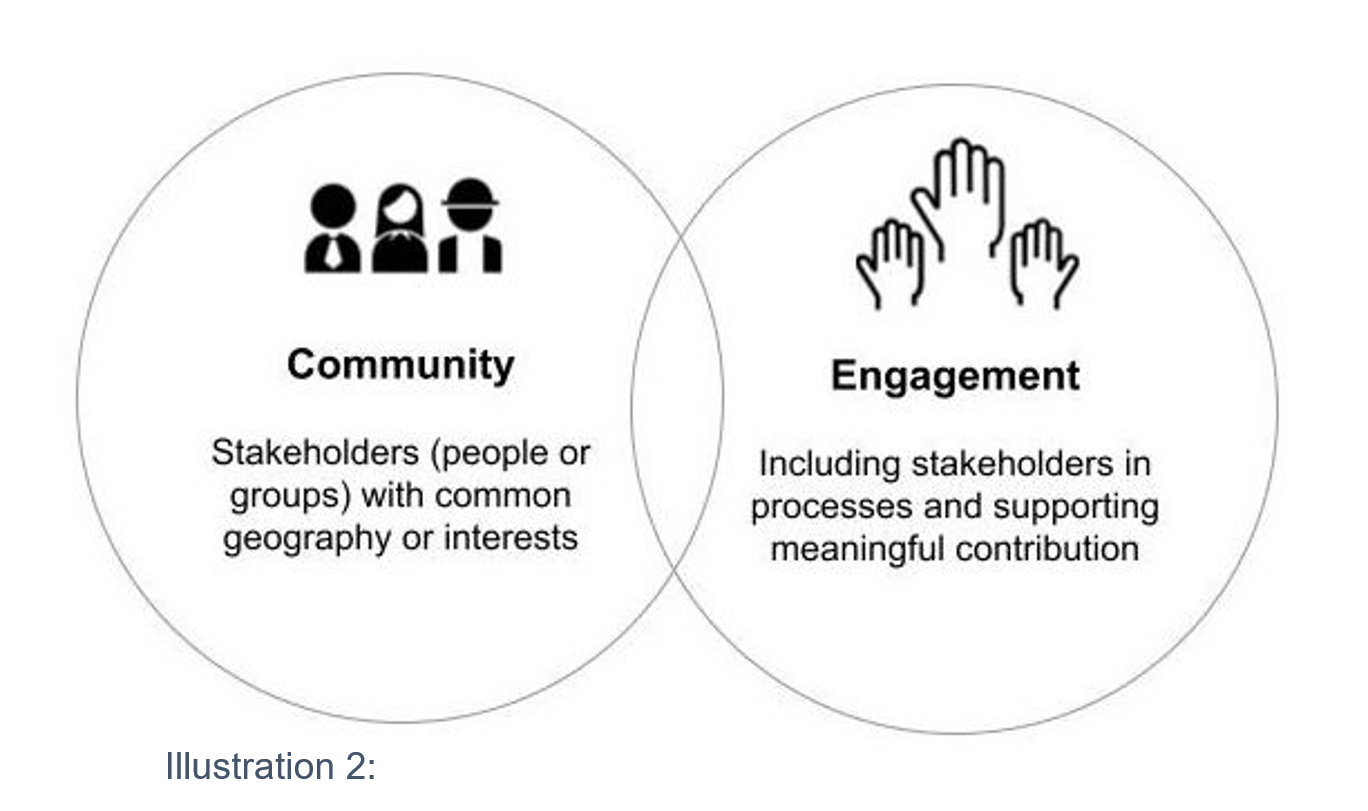
 Community engagement and involvement Community engagement and involvement

Understanding Community Engagement

Strategies for Effective Community Engagement
 1. Building Trust and Relationships: 2. Inclusive Participation: 3. Collaborative Planning: 4. Education and Capacity Building: 5. Leveraging Technology:
Examples of Community Engagement Initiatives

Benefits of Community Engagement
 1. Enhanced Trust: Building trust between community members and institutions leads to more effective and accepted interventions. Challenges and Considerations

Source Source
 Source 1: https://www.hypergene.com/resources/blog/business-model-what-it-is-and-how-you-create-one/ Source 2: https://simplystakeholders.com/what-is-community-engagement/ Source 5: https://practicebusiness.co.uk/making-difficult-decisions-considerations-and-challenges-to-consider |
Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function abajo_pl() in /var/www/vhosts/uprural.eu/httpdocs/ficha_pl.php:1037 Stack trace: #0 {main} thrown in /var/www/vhosts/uprural.eu/httpdocs/ficha_pl.php on line 1037

 Play Audio
Play Audio 

 Introduction to the topic
Introduction to the topic  30 minutes
30 minutes

 Empowerment:
Empowerment: