|
What to know before starting? What to know before starting?
 What will you learn? How much time will it take? EQF level Let’s understand the EU Green Deal
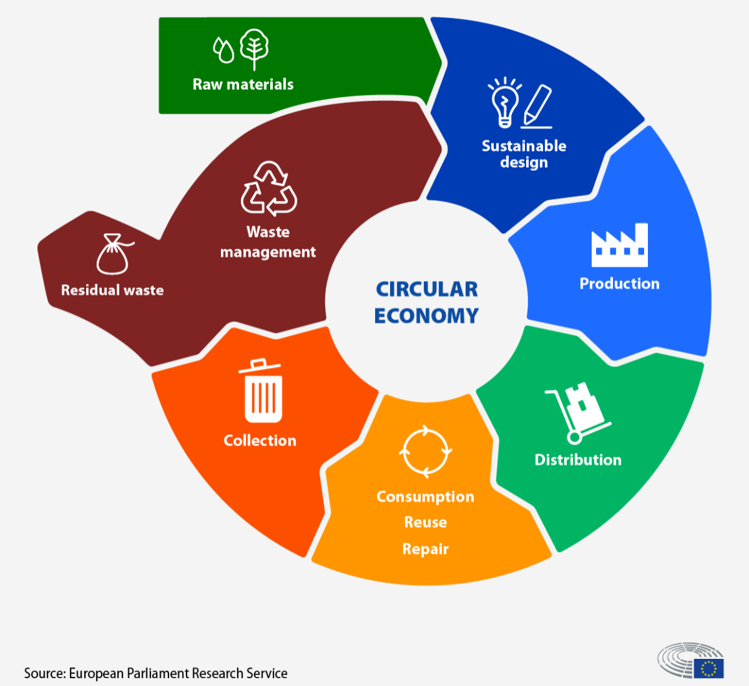
 The “Circular Economy” Model The “Circular Economy” Model
 DEFINITION: it is a model of production and consumption that has the objective of extending the life cycle of products, in order to minimize waste and create more value. The objective is to contrast the linear model of consumption – model based on products of limited lifespan that encourage consumers to buy again. These products are often produced in large quantities with easily accessible materials and energy. The circular economy model is at the basis of the EU Green Deal policy.
The 5 R principle
 The concept of the circular economy is based on the “5 R principle”. Reduce: limited resources means to reduce consumption and chose alternatives like rent or borrow when possible. Reuse: the circular economy model is based on the idea of creating items that can be used in different way to extend their lifecycle. Adapting items to different uses is crucial for this type of model. Repair: the model wants to promote the creation of items with materials that can be replaced, giving new life to items and avoid over-consumption. Rethink: the model wants to promote a “think outside the box” scheme thinking for alternative uses of items to reduce consumption. Recycle: Used materials that are considered waste should be recycled to be able to be transformed in new ones. The Benefits of the Circular Economy

Think: can you think of other benefits the circular economy can bring? Circular Economy in Rural Areas
 The current economic and production systems are very dependent from the environment. Circular economy consider waste a crucial resource that must be integrated. Application of this model requires the collaboration of people, policies and places:
Rural areas can benefit from the application of this model in terms of:
The Product as Service Model (PaaS) The Product as Service Model (PaaS)

.
The PaaS Model in Rural Areas
 This model in rural areas can help:
Practical examples:
Sources Sources
 https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/bee1dd72-en/index.html?itemId=/content/component/bee1dd72-en https://www.regeneration2030.org/post/the-great-five-r-s-of-circular-economy https://multitraces.ub.ro/files/IO/IP1/O1_Chapter_2_Circular_economy_in_rural_areas_R.pdf https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/markets-and-consumers/energy-communities_en https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/circular-examples/the-eus-circular-economy-action-plan | ||||||||||
The tutor has to engage the participants in all times. It is important to always keep attention and motivation high. The use of digital tools or other resources depends on the delivery method chosen and on the characteristics of the participants of the classroom. It is important therefore to understand well the classroom in order to adapt the method of training.
Consortium






 Play Audio
Play Audio 



 Define the circular economy and its core principles.
Define the circular economy and its core principles. 30 minutes
30 minutes